Recent News

NGC 1851 is a massive globular cluster located in the Southern constellation of Columba. It is an unusual cluster speculated to be a product of the merger of two individual clusters. It has been known to have a bimodal horizontal branch in the H-R diagram. In this color-composite image, the blue dots are the Blue horizontal branch stars mostly distributed in the 2.4 arcmin radius of the cluster. These stars have evolved off the red-giant branch phase and are now burning helium in their cores.
Credits: UVIT Team/ISRO/CSA
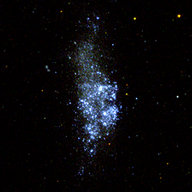
WLM (Wolf-Lundmark-Melotte) is a dwarf irregular galaxy of the Local Group located at a distance of 995 kpc. The galaxy is known as ’living cosmic fossil’ as it has formed during the early epoch of universe and has not interacted with other galaxy so far. The bright blue sources are the recent star forming regions of the galaxy. The point sources seen in the image are actually star clusters or stellar groups of the galaxy. This is a false color composite image of the galaxy where FUV and NUV are displayed by blue and yellow color respectively.
Credits: UVIT Team/ISRO/CSA

NGC 362 is a globular cluster in the constellation Tucana, in the northern edge of our satellite galaxy known as the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC). The tightly packed stars which appear as white spot in the image form the core of the cluster. The light blue dots surrounding the cluster core are extreme horizontal branch stars. The bright blue dots scattered all over the image are hot, young stars in the SMC. This is a false color composite image, where the light detected by the FUV and NV channels of the UVIT are colored in blue and yellow respectively.
Credits: UVIT Team/ISRO/CSA




